Polycystic Kidney Disease Histology
Polycystic kidney disease histology. Patients had either serum creatinine SCr below 350 mumolliter N 12 or terminal renal failure N 50. Minority of cases gene unmapped OMIM 600666 10 lack a family history and are considered new mutations. ADPKD may associate some other extrarenal abnormalities such as.
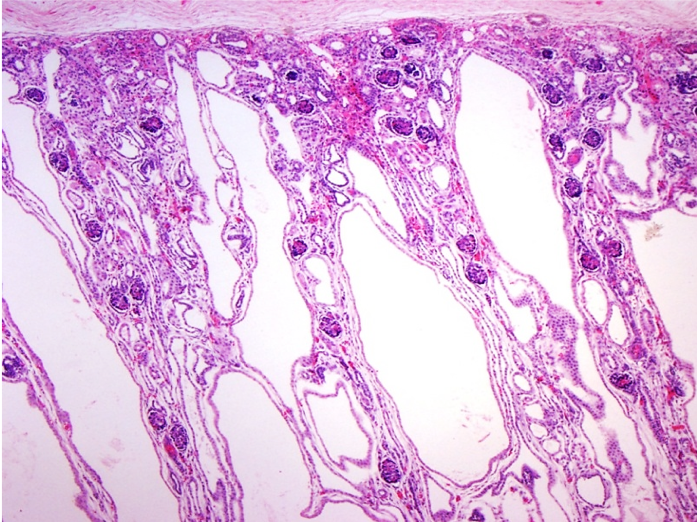
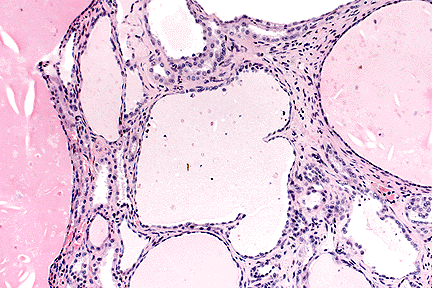
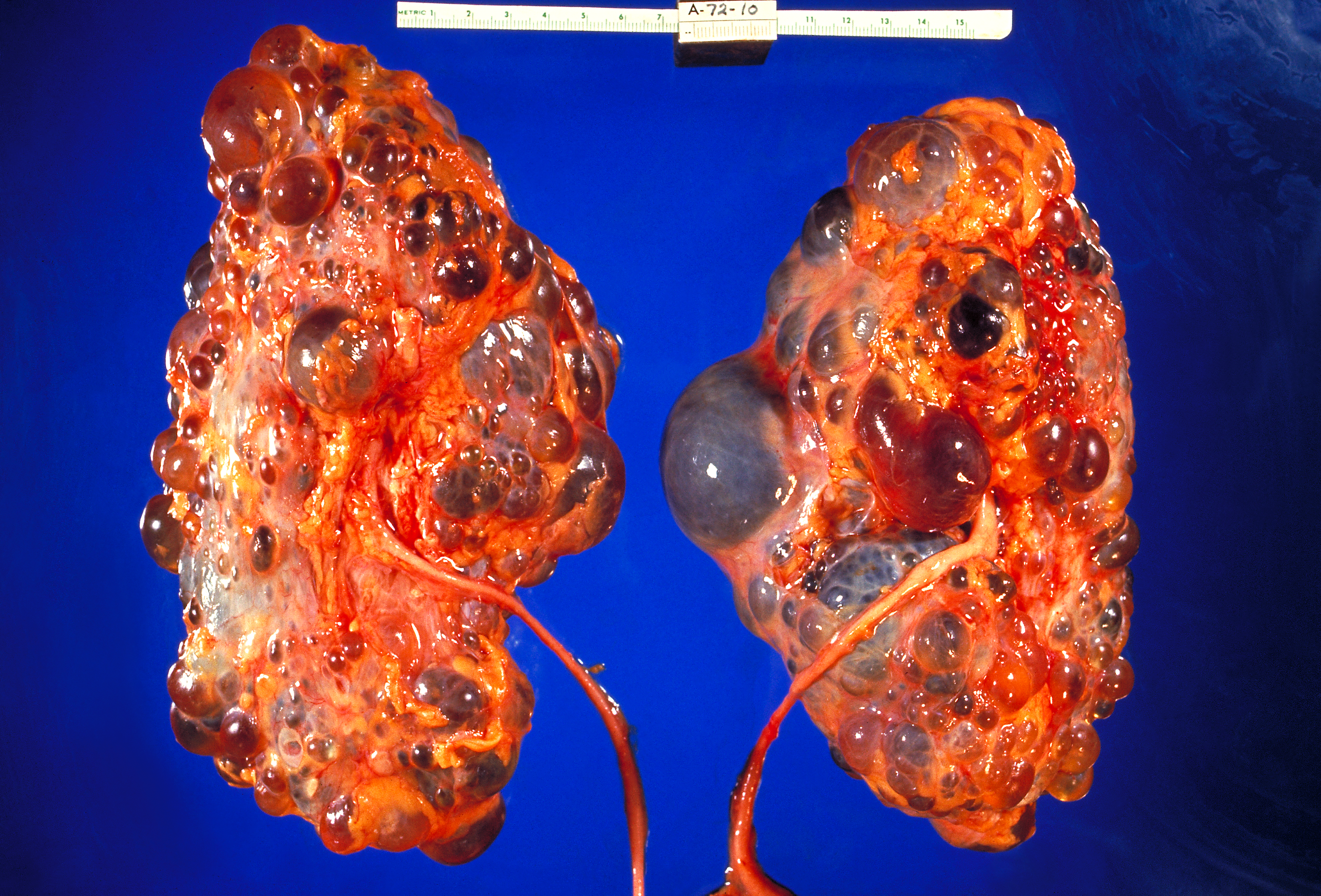
Renal specimens were obtained at surgery or postmortem from patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD. The abnormalities that develop in this disease vary greatly and there are no disease-specific treatments at this time. Polycystic kidney adult type is a manifestation of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease caused by mutations in genes on chromosome 16p133 PKD1 - producing protein Polycystin 1 and 4q21 PKD2 - Polycystin 2.
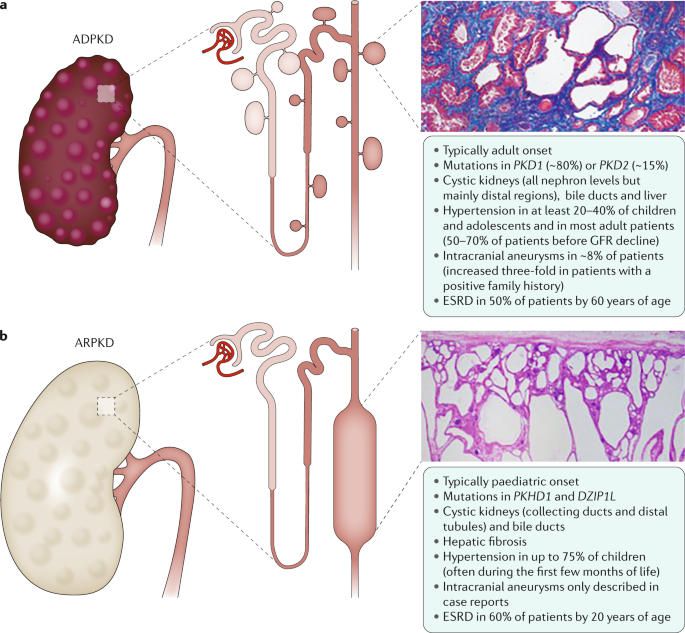
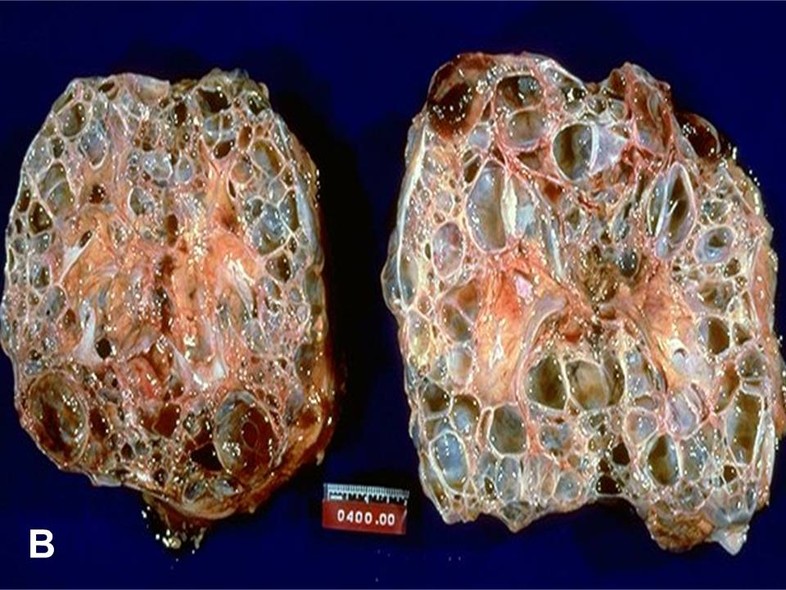
Polycystic kidney disease PKD a common genetic cause of chronic renal failure is characterized by accumulation of fluid filled cysts in the kidney and other organs. ARPKD is relatively uncommon and occurs primarily in neonates and children. From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most prevalent potentially lethal monogenic human disorder.
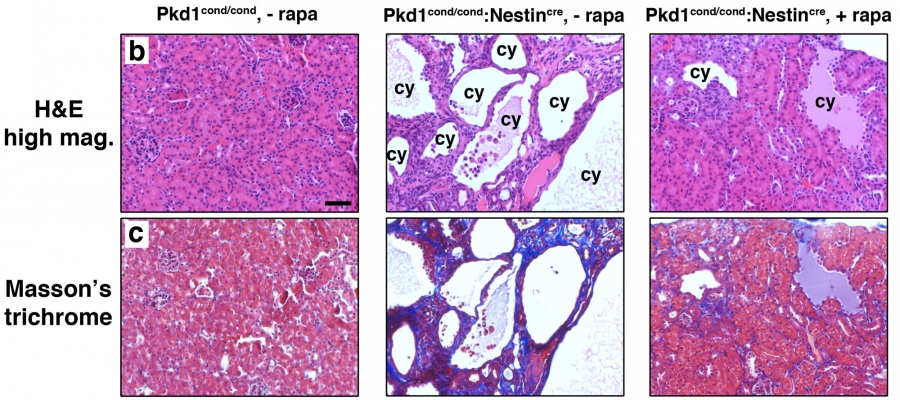
Mutations in PKHD1 gene Polycystic Kidney and Hepatic Disease 1 produces fibrocystin polyductin at 6p12 expressed in kidney pancreas and liver Braz J. PKD can be inherited as an autosomal recessive ARPKD or autosomal dominant trait ADPKD. Renal histology in polycystic kidney disease with incipient and ad-vanced renal failure.
Epedemiology 125 million people in the world 3. In 68 of the cats presented with polycystic kidneys there were also cystic changes of the liver uni- or multilocular cysts andor congenital hepatic fibrosis CHF. Histopathology Kidney--Adult polycystic disease About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features 2021 Google LLC.
PKD2 gene on 4q13-23 altered in 10 of cases produces polycystin 2. Polycystic kidney disease abbreviated PKD may refer to a number of conditions in the kidney characterized by cysts. Renal specimens were obtained at surgery or postmortem from patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD.
Polycystic Kidney disease 1. Pathology Outlines Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney.
ARPKD is relatively uncommon and occurs primarily in neonates and children.
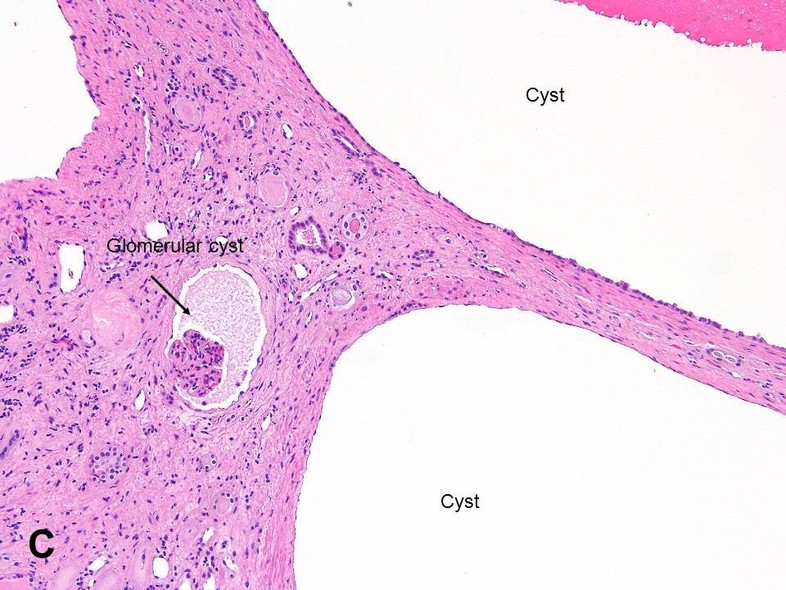
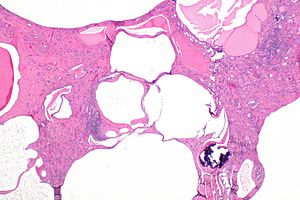
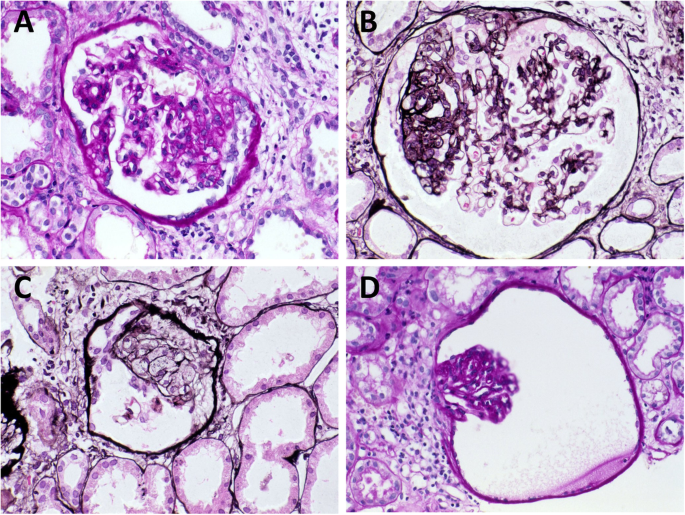
PKD2 gene on 4q13-23 altered in 10 of cases produces polycystin 2. Polycystic Kidney disease 1. Renal histology in polycystic kidney disease with incipient and advanced renal failure. Polycystic kidney disease PKD a common genetic cause of chronic renal failure is characterized by accumulation of fluid filled cysts in the kidney and other organs. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is a multisystemic and progressive disorder characterized by cyst formation and enlargement in the. Numerous and are fluid-filled resulting in massive enlargement of the kidneys. Polycystic kidney disease typically refers to one of the following. Renal specimens were obtained at surgery or postmortem from patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD. Polycystic kidney disease abbreviated PKD may refer to a number of conditions in the kidney characterized by cysts.
Numerous and are fluid-filled resulting in massive enlargement of the kidneys. It is associated with large interfamilial and intrafamilial variability which can be explained to a large extent by. From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD is the most prevalent potentially lethal monogenic human disorder. Patients had either serum creatinine S below 350 molliter N 12 or terminal renal failure N 50. Renal specimens were obtained at surgery or postmortem from patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD. Patients had either serum creatinine S C r below 350 µmolliter N 12 or terminal renal failure N 50. Polycystic Kidney disease 1.







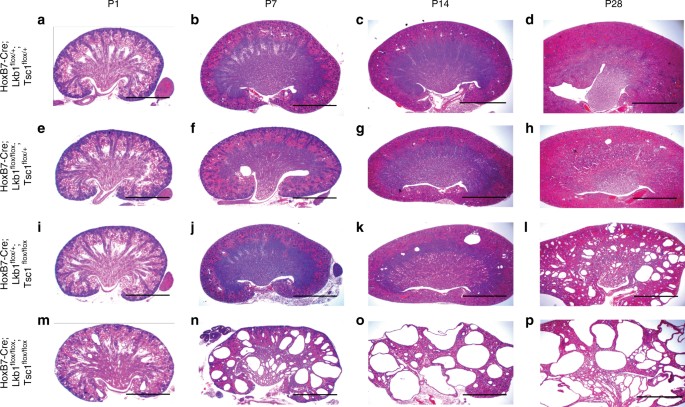









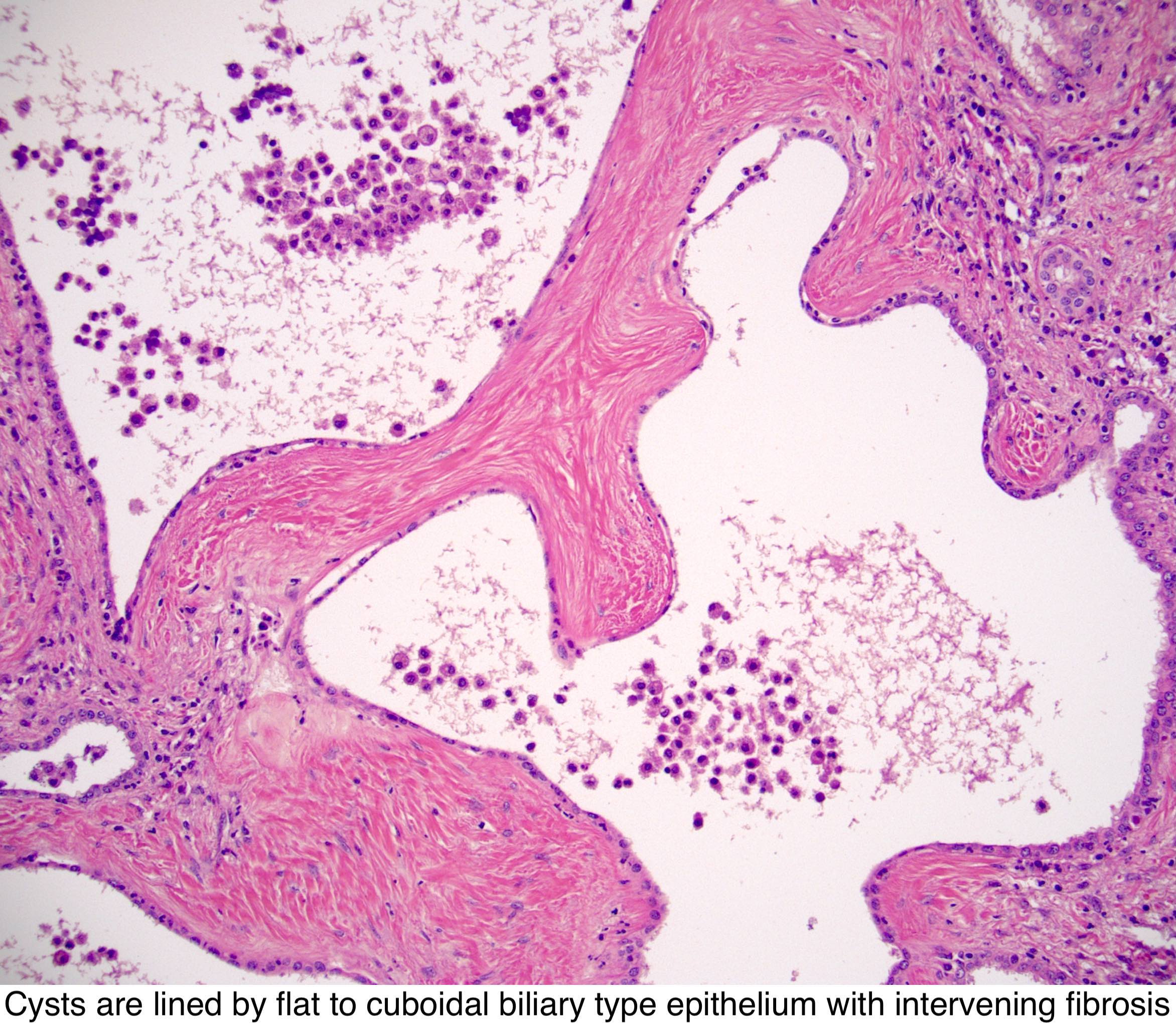

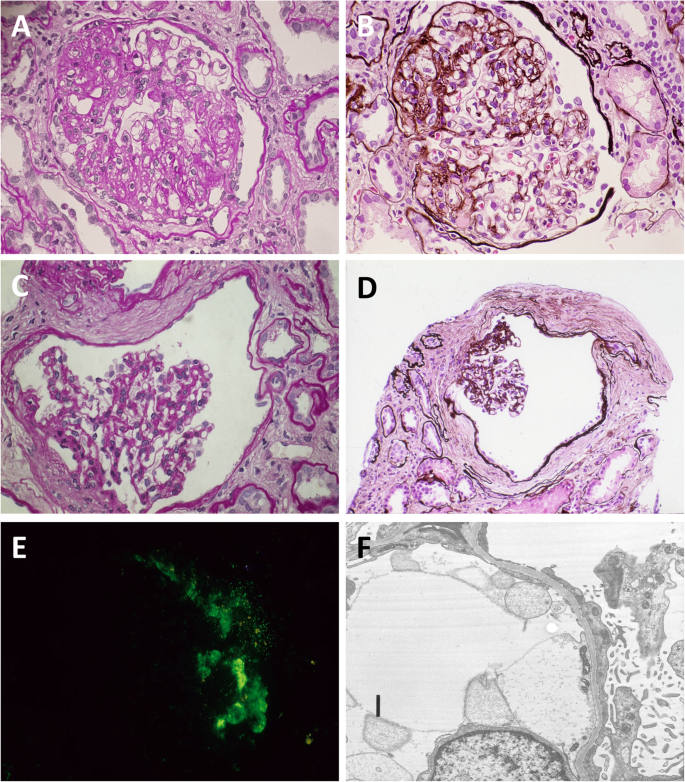

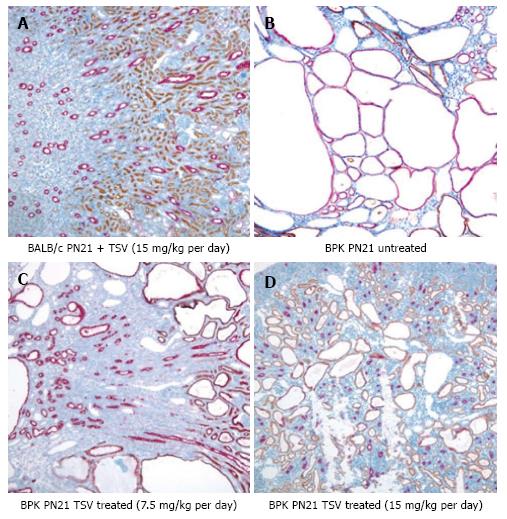







Posting Komentar untuk "Polycystic Kidney Disease Histology"