Epidemiology Of Celiac Disease
Epidemiology of celiac disease. Contrary to common belief gluten enteropathy is a systemic disease rather than merely an ailment of the alimentary tract. However the diagnostic rate is still very low in these countries. Using a large database we sought to describe the epidemiology of several psychiatric disorders in CD.
Celiac disease CD is a chronic disorder resulting from an immune reaction to gluten in genetically predisposed individuals. The CD-related enteropathy is characterized by small intestinal villous atrophy and crypt hyperplasia. Epidemiology of celiac disease.
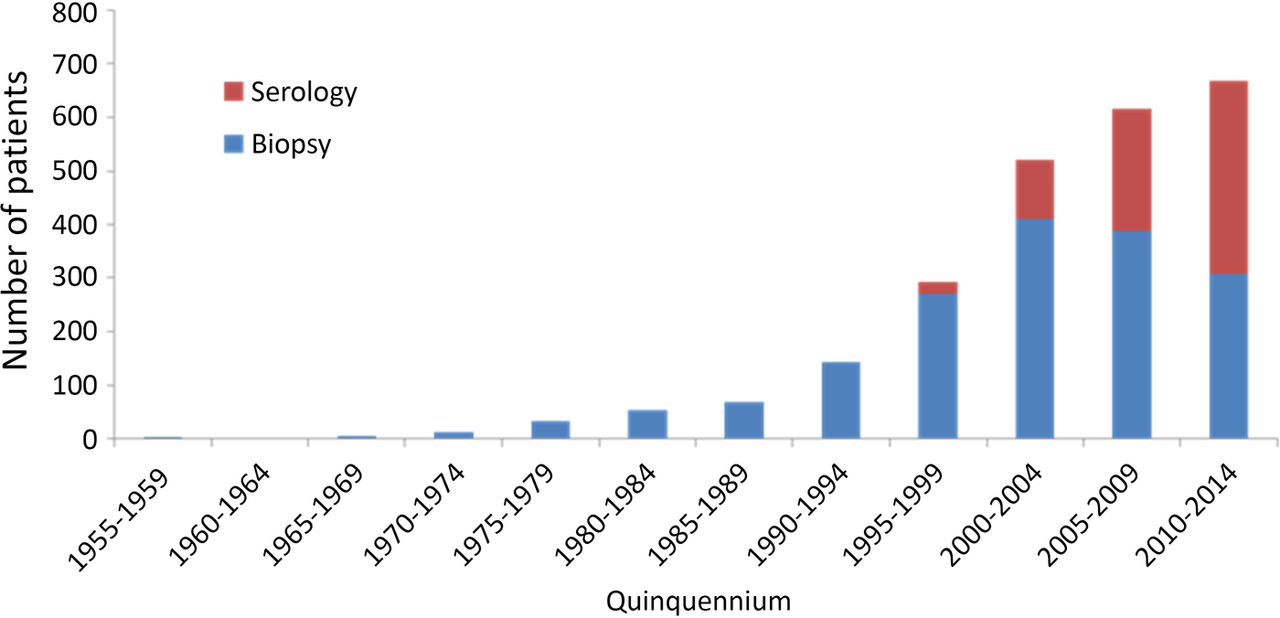
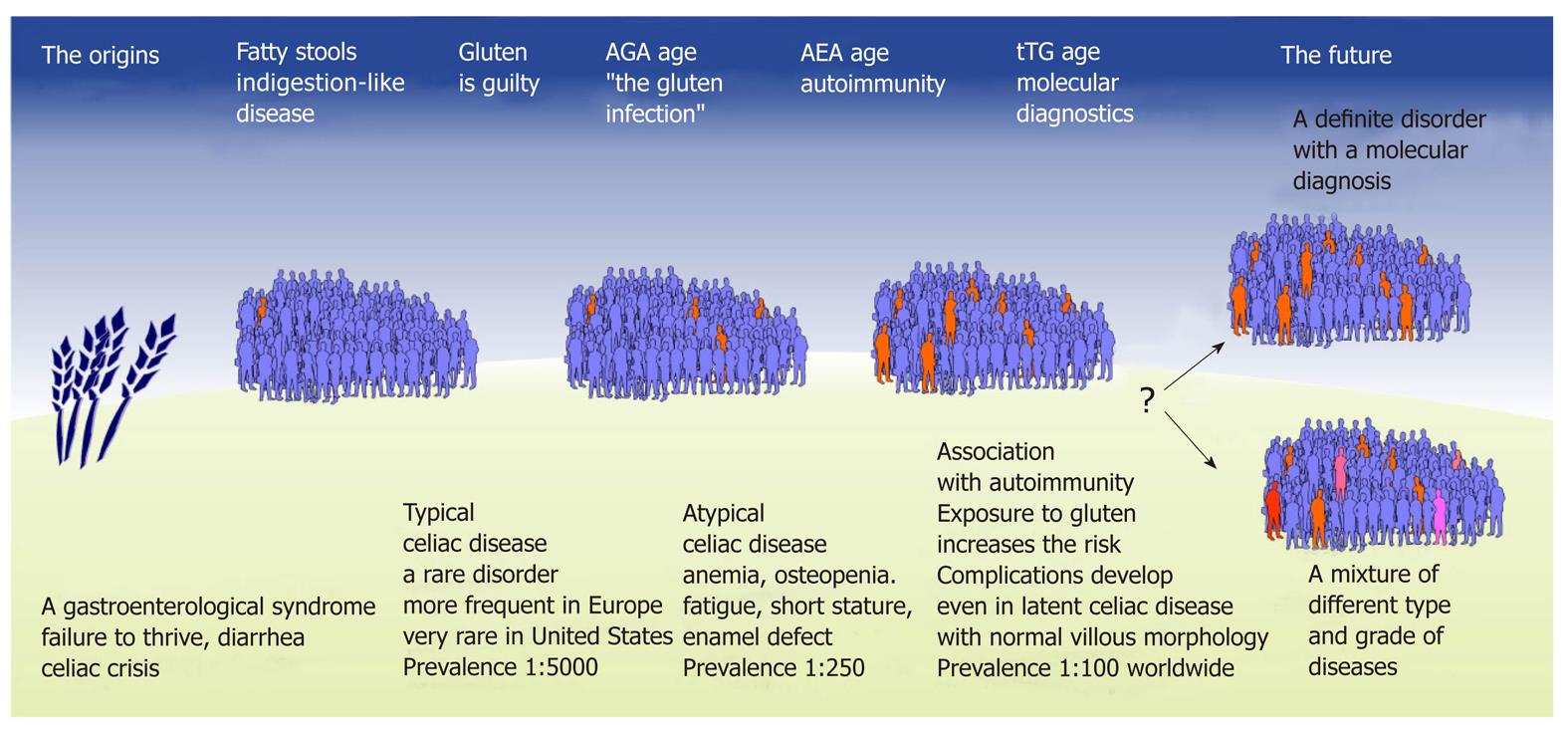
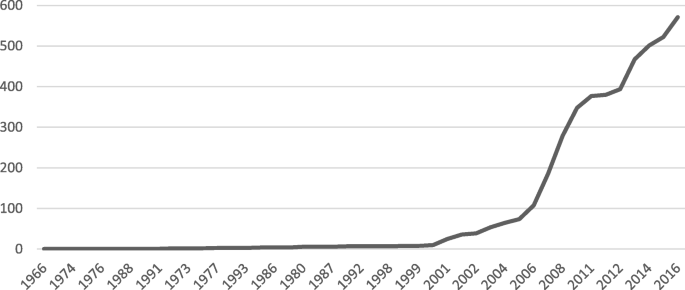
The rise in incidence is also due to a real increase of this immune-based disorder independent of disease detection. Epidemiology Presentation and Diagnosis of Celiac Disease The incidence of celiac disease is increasing partly due to improved recognition of and testing for the disease. In 1887 Samuel Gee described typical symptoms of celiac disease in children including irritability chronic diarrhea and failure to thrive and cure by means of a diet was suggested for the first.
The disease epidemiology reported from these areas largely overlaps with European and American data. The most recent analysis of celiac disease prevalence in the United States based on NHANES found that the prevalence of celiac disease remained stable from 2009 to 2014 at 07 but that the proportion of patients with celiac disease who remain undiagnosed has decreased over time. Gluten is a protein component found in wheat barley and rye but not in oats.
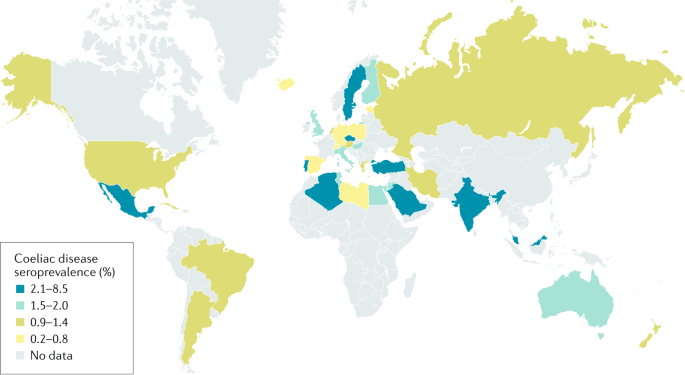
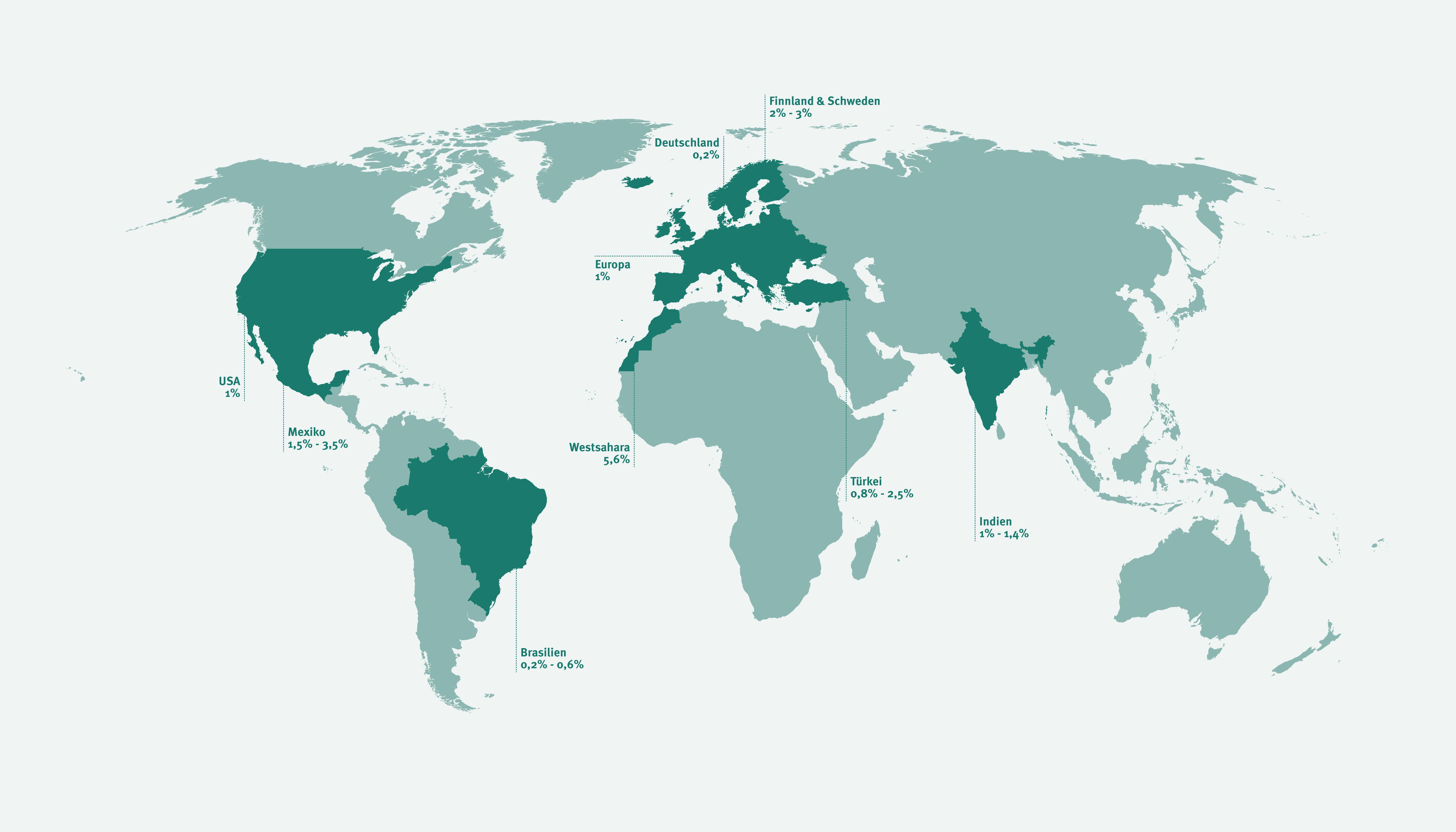
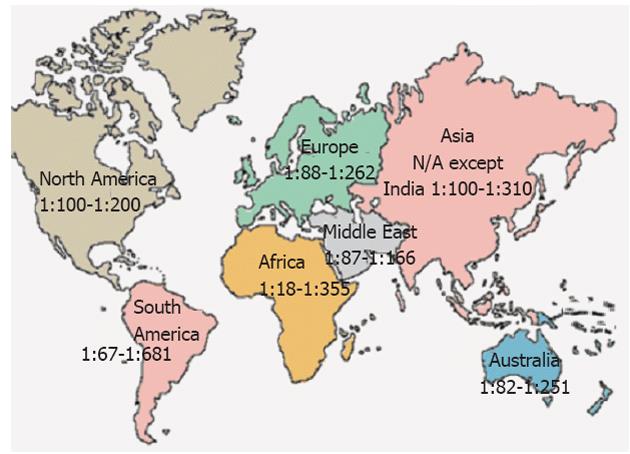
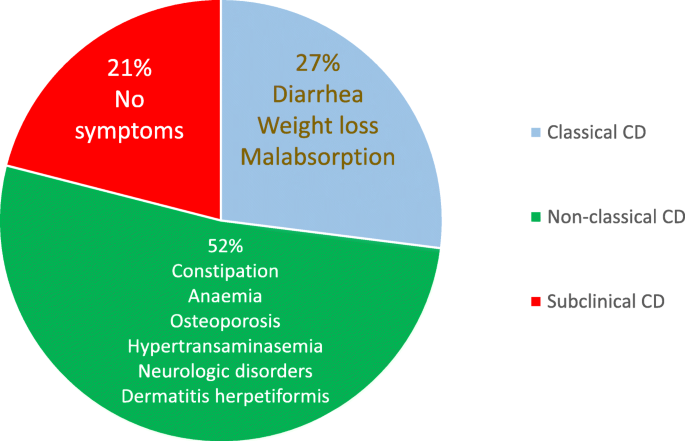
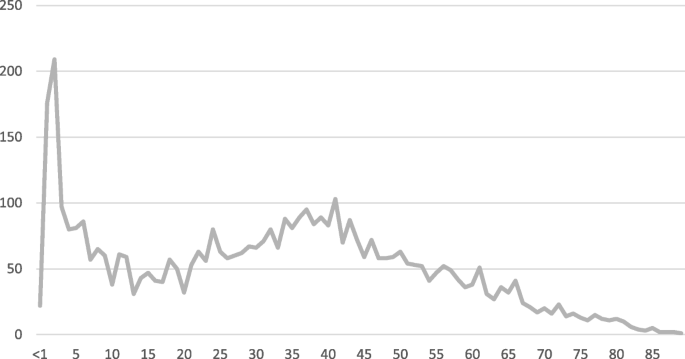
Celiac disease occurs in adults and children at rates approaching 1 of the population and is recognized around the world. KW - Celiac disease. This data was based on the occurrence of manifest disease and more classical presentation forms of celiac disease.
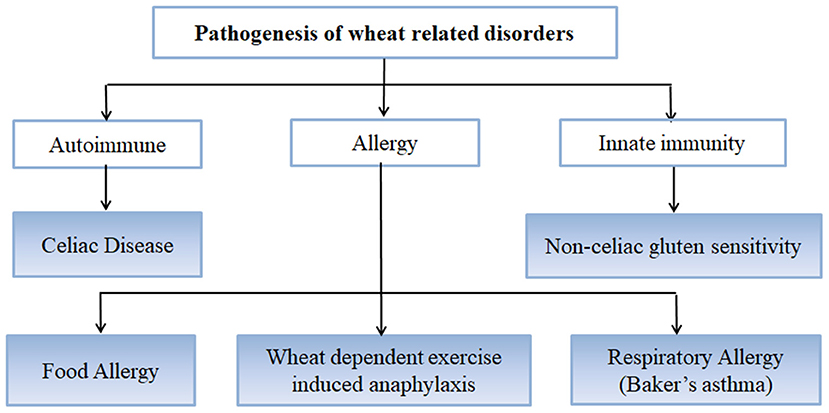
CD usually responds to a glutenfree diet GFD. Celiac disease CD is characterized by changes in duodenal and small bowel mucosa that are caused by gluten intolerance. CD is a common disorder in north Africa and Middle East countries as well.
Celiac disease was long regarded as a rare childhood disease. Comment on Am J Gastroenterol.
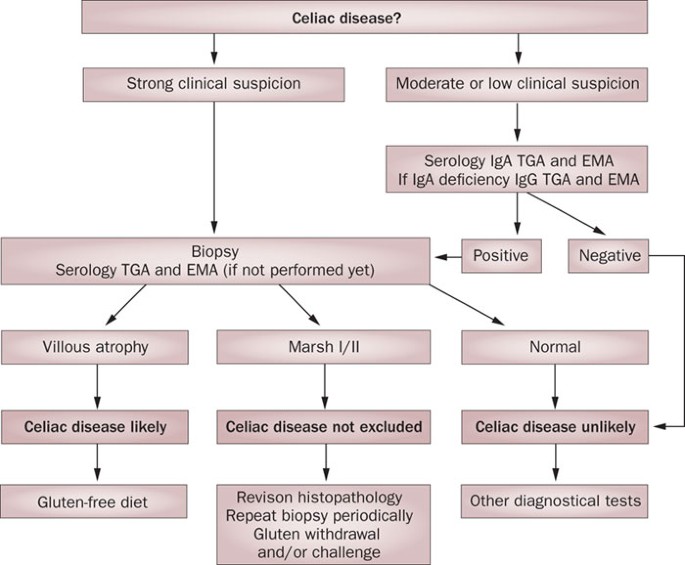
These changes include an increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes partial or complete villous atrophy and hypoplasia of the small bowel architecture.
Epidemiology Presentation and Diagnosis of Celiac Disease The incidence of celiac disease is increasing partly due to improved recognition of and testing for the disease. Print. Epidemiology of celiac disease. There is interest in identifying aspects of the microbiome associated with the development of celiac disease because this may be a modifiable risk factor55Epidemiology studies found associations between antibiotic use56and elective cesarian birth45with celiac disease so the increase in celiac disease incidence might involve changes in the microbiome caused by these practices. These changes include an increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes partial or complete villous atrophy and hypoplasia of the small bowel architecture. Celiac disease CD is a chronic disorder resulting from an immune reaction to gluten in genetically predisposed individuals. The disease epidemiology reported from these areas largely overlaps with European and American data. This Celiac Disease CD - Market Insights Epidemiology and Market Forecast- 2030 report delivers an in-depth understanding of the Celiac Disease CD historical and forecasted epidemiology as. Epidemiology Presentation and Diagnosis of Celiac Disease The incidence of celiac disease is increasing partly due to improved recognition of and testing for the disease.
The most recent analysis of celiac disease prevalence in the United States based on NHANES found that the prevalence of celiac disease remained stable from 2009 to 2014 at 07 but that the proportion of patients with celiac disease who remain undiagnosed has decreased over time. Towards explaining the Swedish epidemic of celiac disease - an epidemiological approach in Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine Epidemiology and Global Health. There is interest in identifying aspects of the microbiome associated with the development of celiac disease because this may be a modifiable risk factor55Epidemiology studies found associations between antibiotic use56and elective cesarian birth45with celiac disease so the increase in celiac disease incidence might involve changes in the microbiome caused by these practices. There have been substantial increases in prevalence and incidence over the last 2 decades for reasons that are almost certainly environmental but for which there is no clarity as to cause. These changes include an increase in intraepithelial lymphocytes partial or complete villous atrophy and hypoplasia of the small bowel architecture. Celiac disease CD is a chronic small intestine immune-mediated enteropathy triggered by exposure to gluten in genetically sensitive individuals DQ2 or DQ8. Celiac disease CD is characterized by changes in duodenal and small bowel mucosa that are caused by gluten intolerance.































Posting Komentar untuk "Epidemiology Of Celiac Disease"