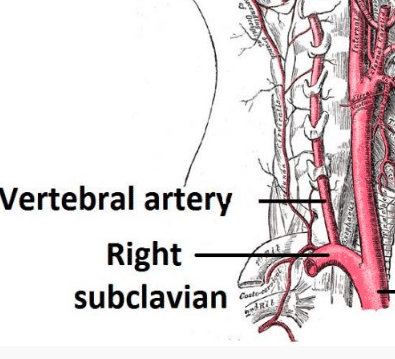
Right Subclavian Steal Syndrome
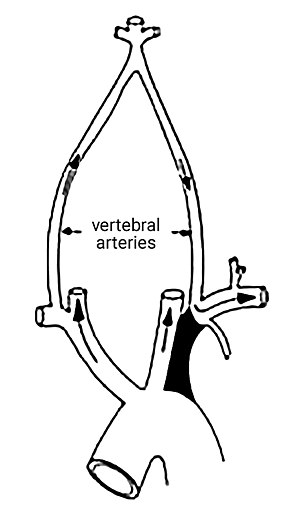
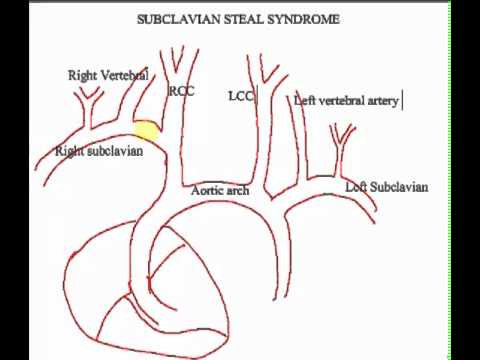
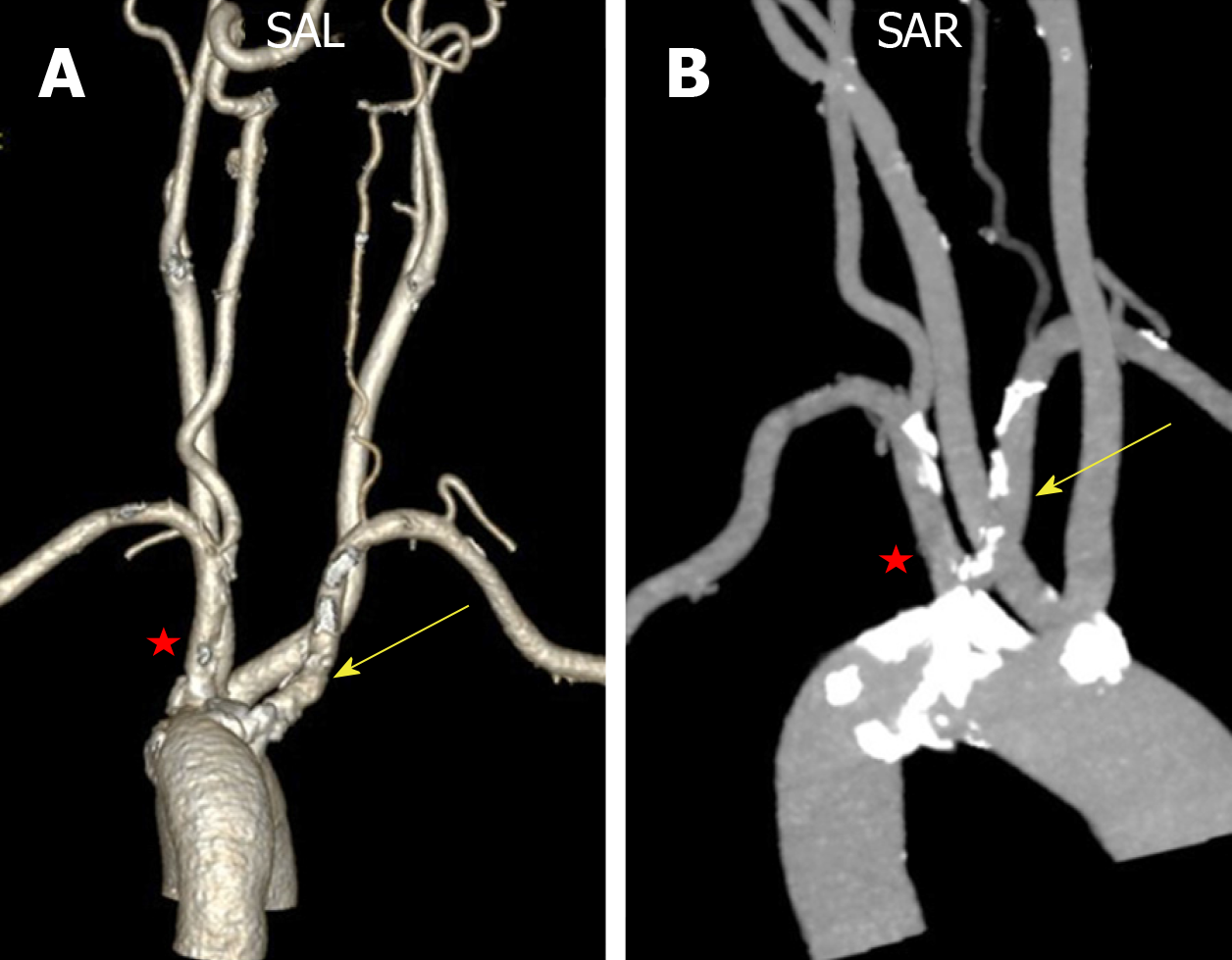
Right subclavian steal syndrome. Although a low-grade stenosis is usually asymptomatic and may remain unobserved a. Report of 3 Cases and Literature Review. In patients with the subclavian steal syndrome occlusion of the subclavian artery or innominate artery proximal to the vertebral artery on that side gives rise to a pressure differential between the two vertebral arteries.
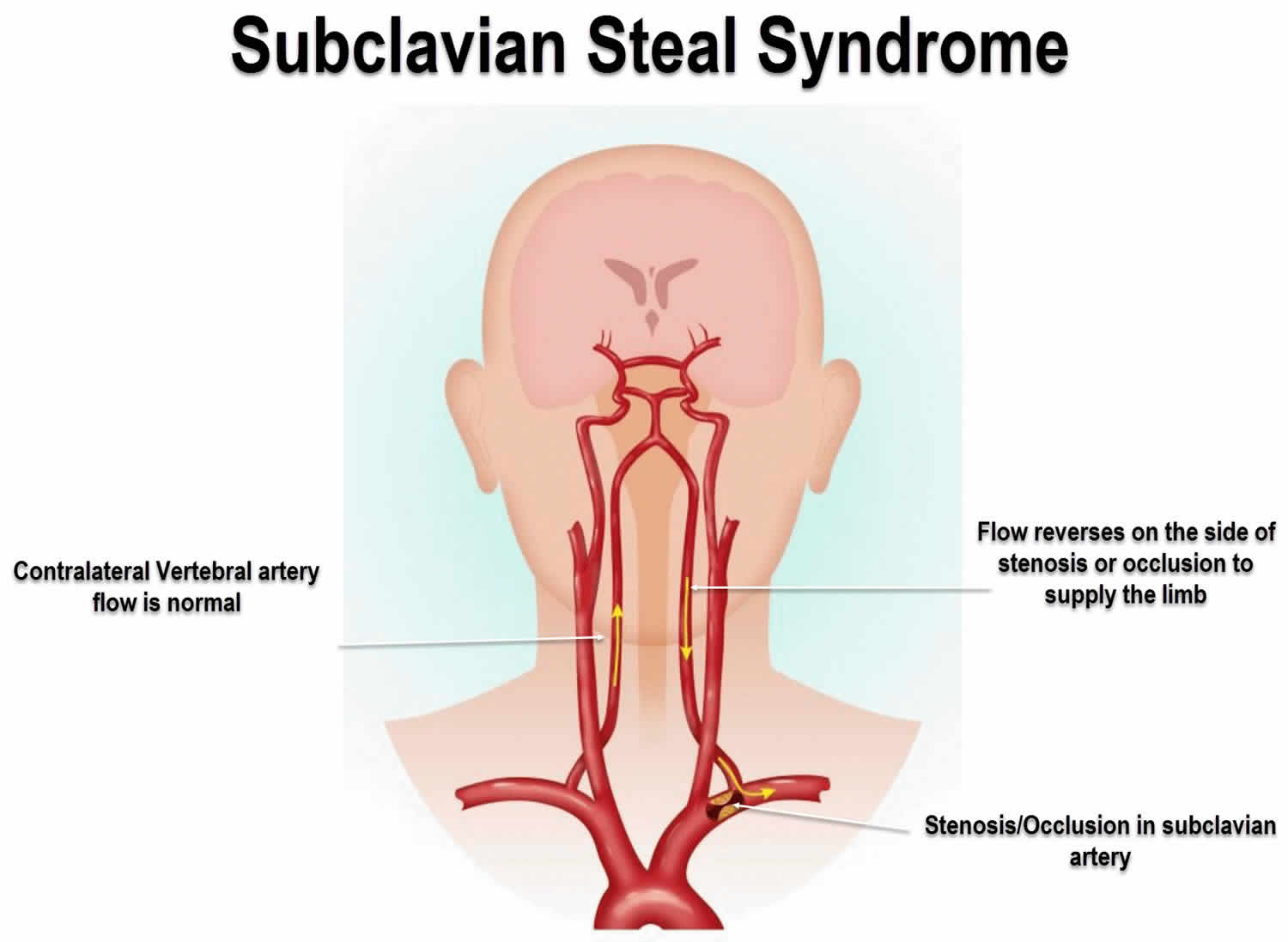
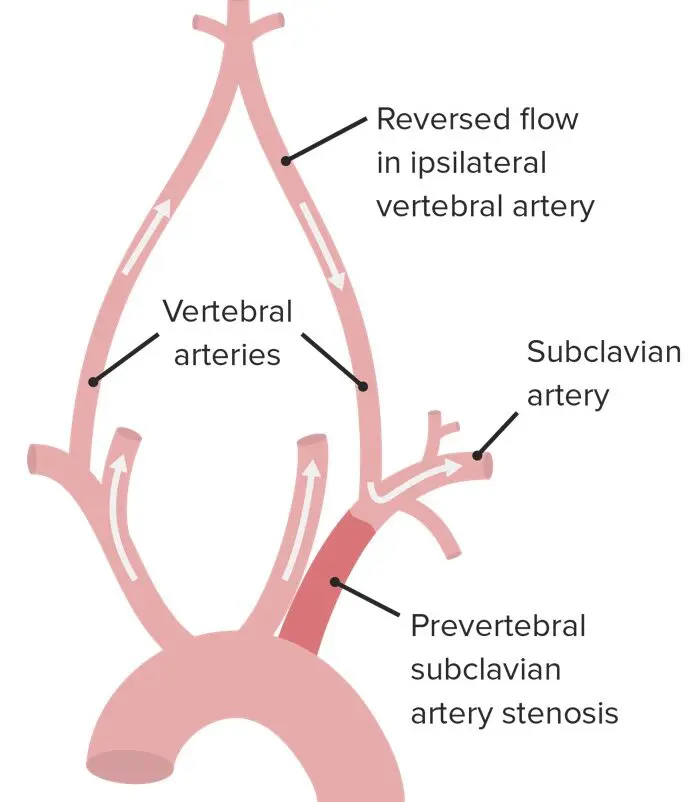
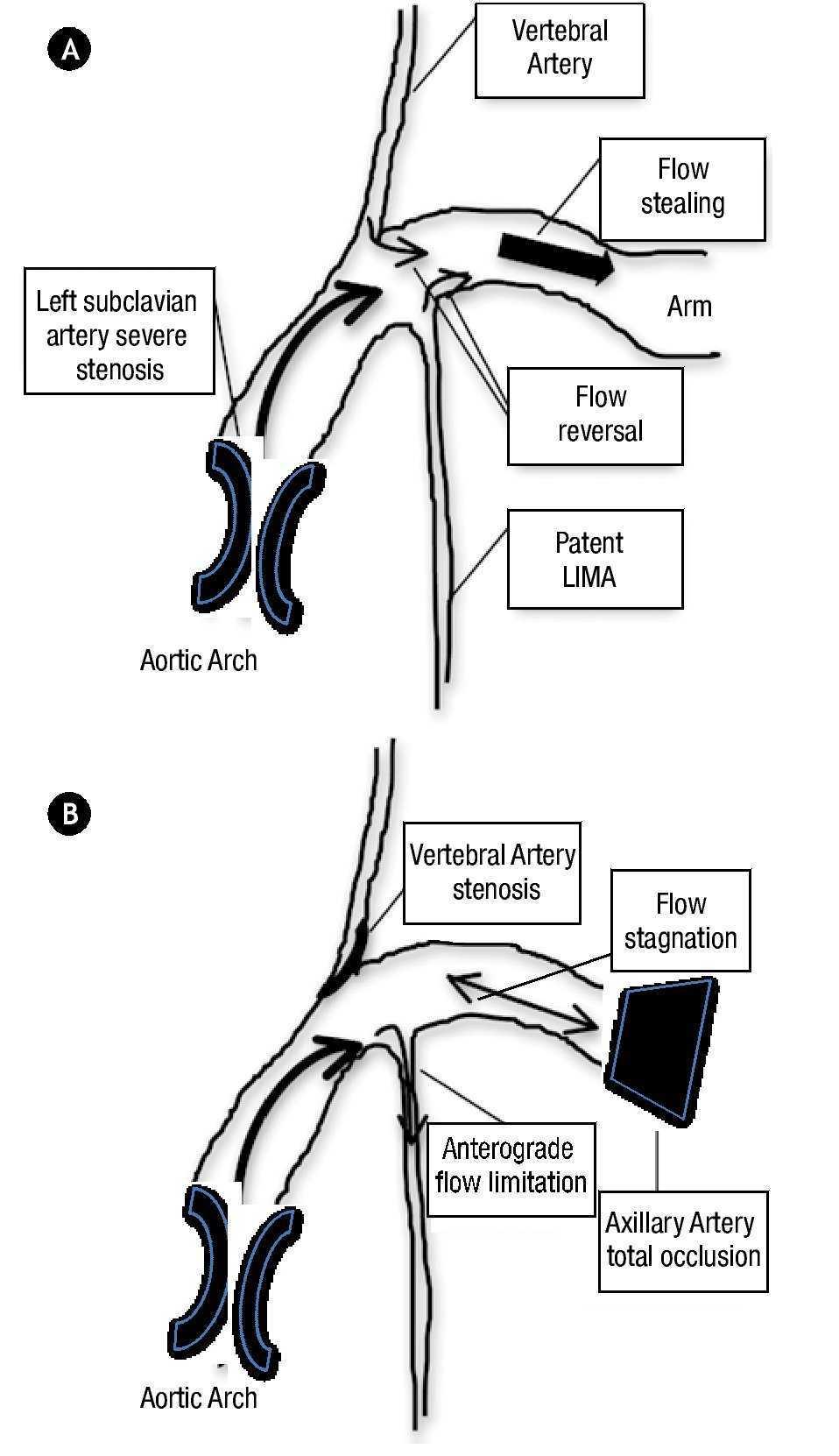
Subclavian steal syndrome is a syndrome associated with steno-occlusive pathology of the proximal subclavian artery with subsequent reversal of flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery. It is characterized by flow reverse in the vertebral artery to supply the vascular bed distal to the occlusionobstruction and to perfuse the arm collateral flow. The subclavian steal syndrome is a rare but important cause of syncope.
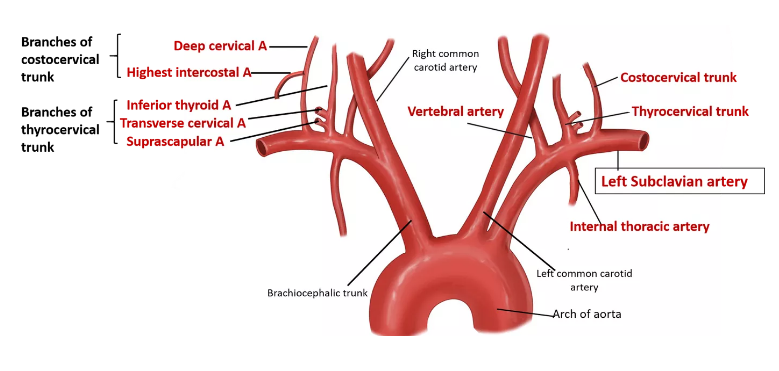
The term subclavian steal describes retrograde blood flow in the vertebral artery associated with proximal ipsilateral subclavian artery stenosis or occlusion usually in the setting of subclavian artery occlusion or stenosis proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. Subclavian artery stenosis is an uncommon vascular disease showing a 4-fold left rather than right-sided predisposition. Symptoms of SSS include vertigo during arm exertion and hand or arm pain and numbness or weakness in the arm involved due to hypoperfusion.
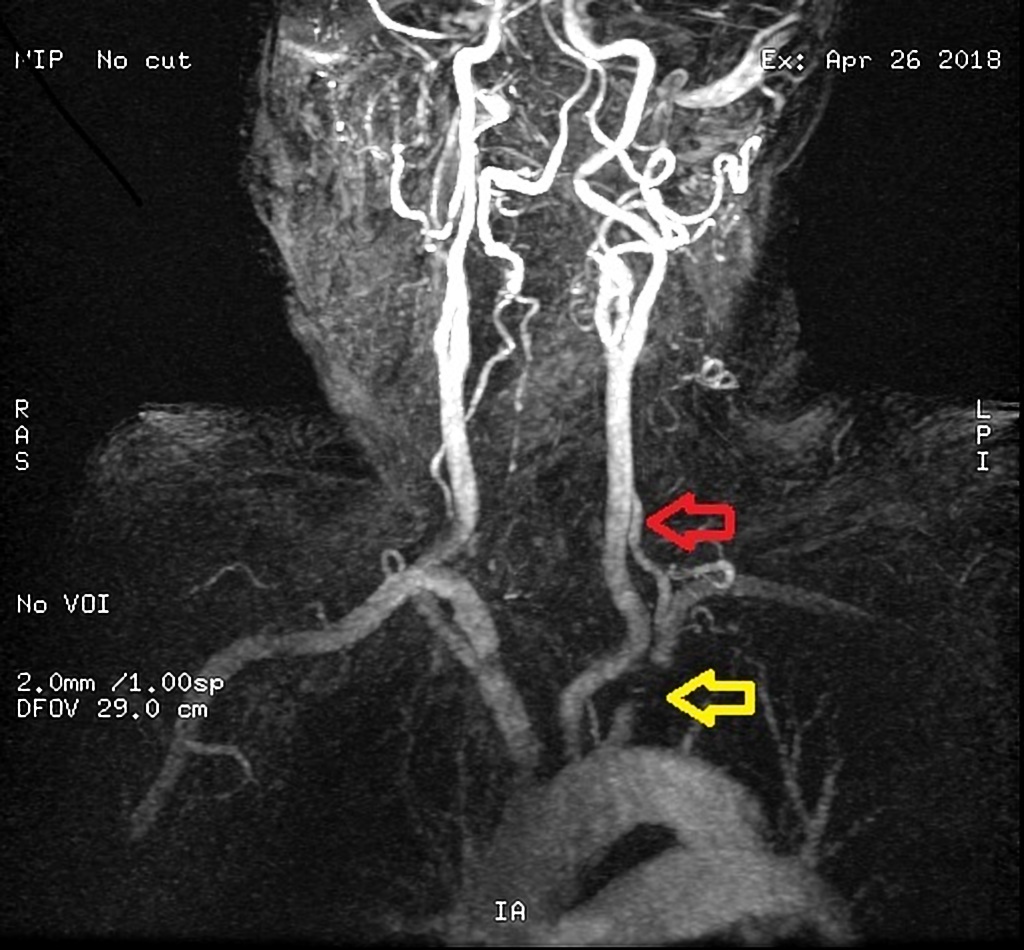
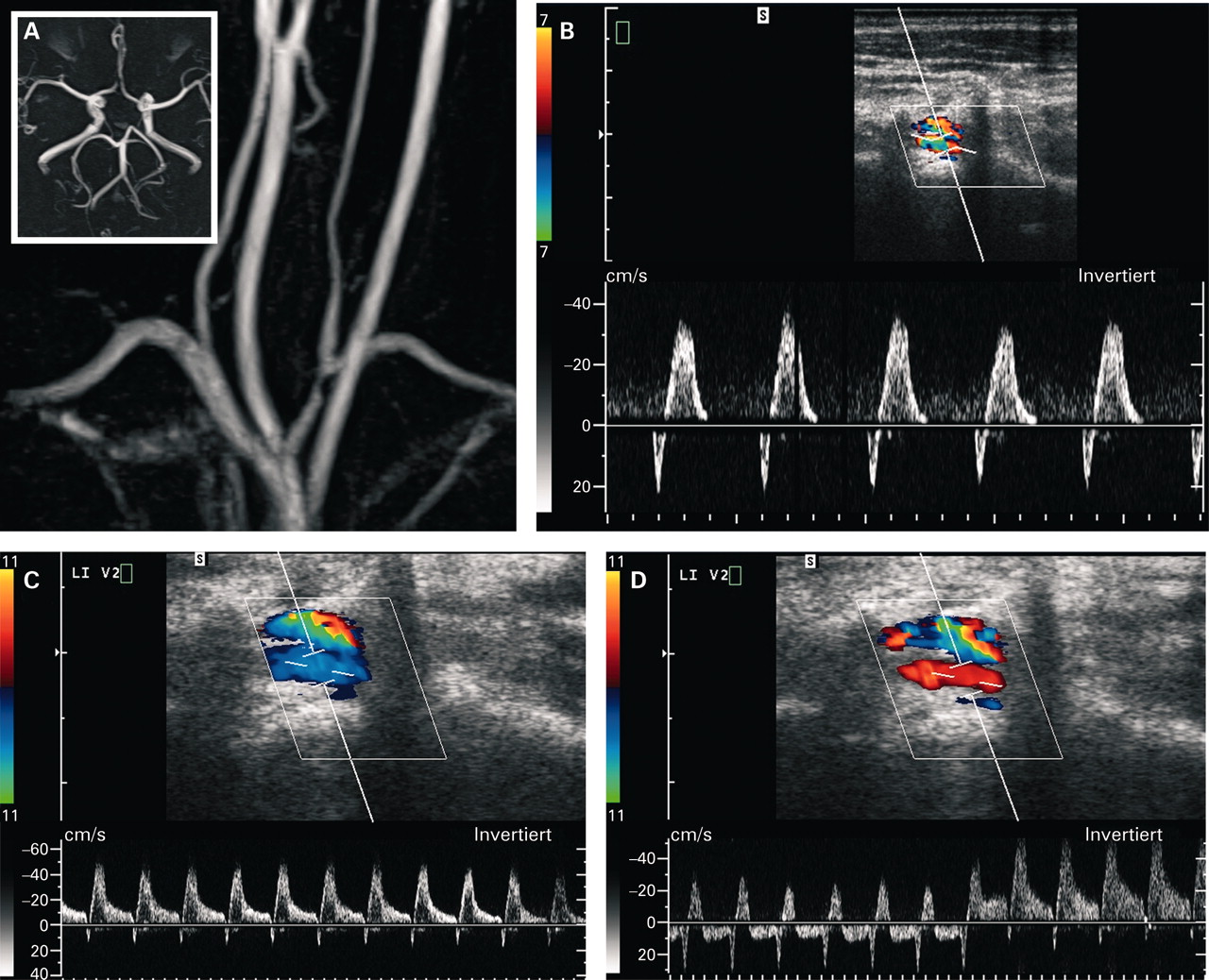
The left vertebral artery spectral wave doppler is seen below the baseline as compared to both left CCA and right vertebral artery. Subclavian steal syndrome occurs secondary to a proximal stenosing lesion or occlusion in the subclavian artery. Features are characteristic of complete left subclavian steal syndrome Features are characteristic of complete left subclavian steal syndrome.
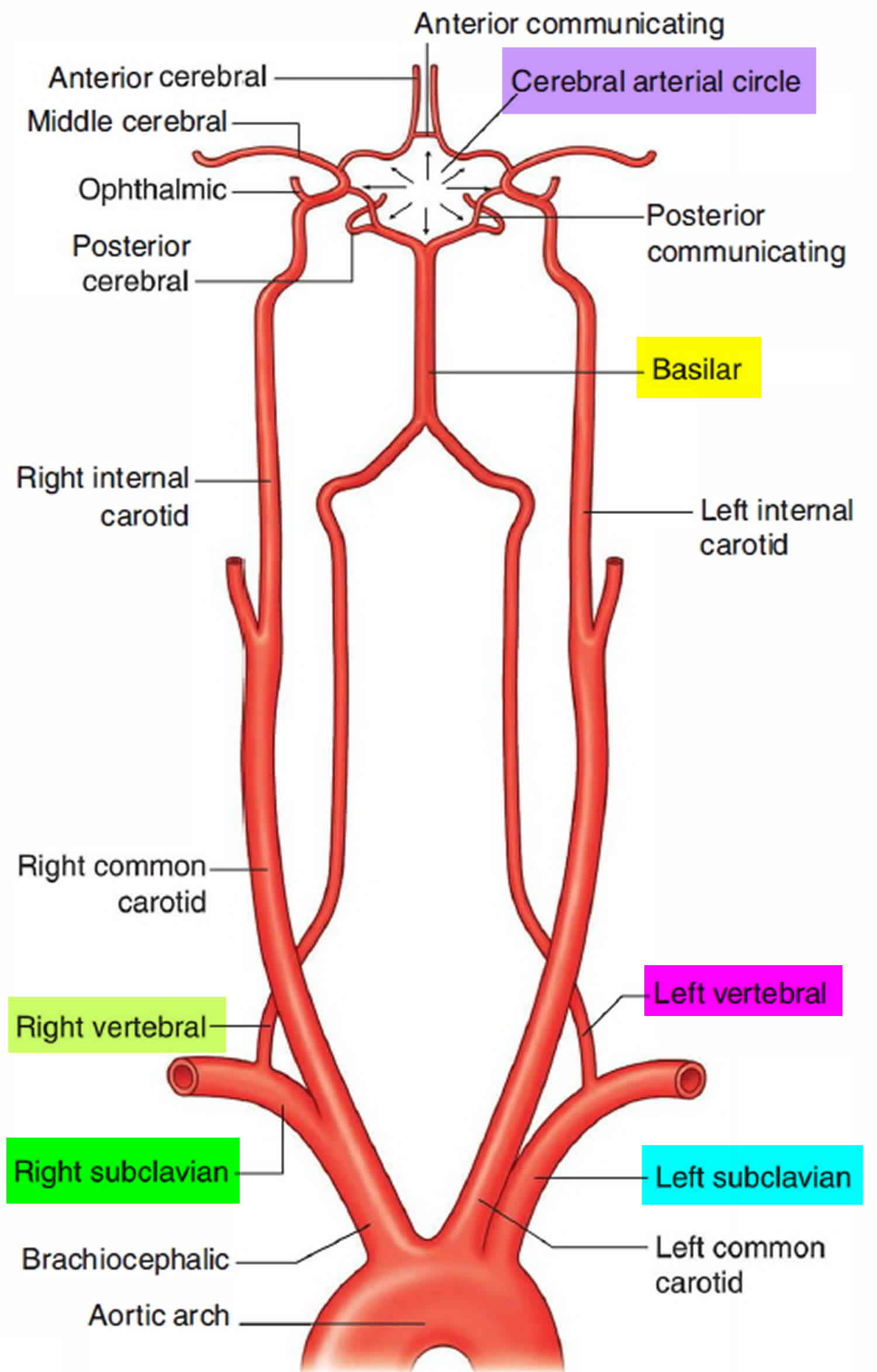
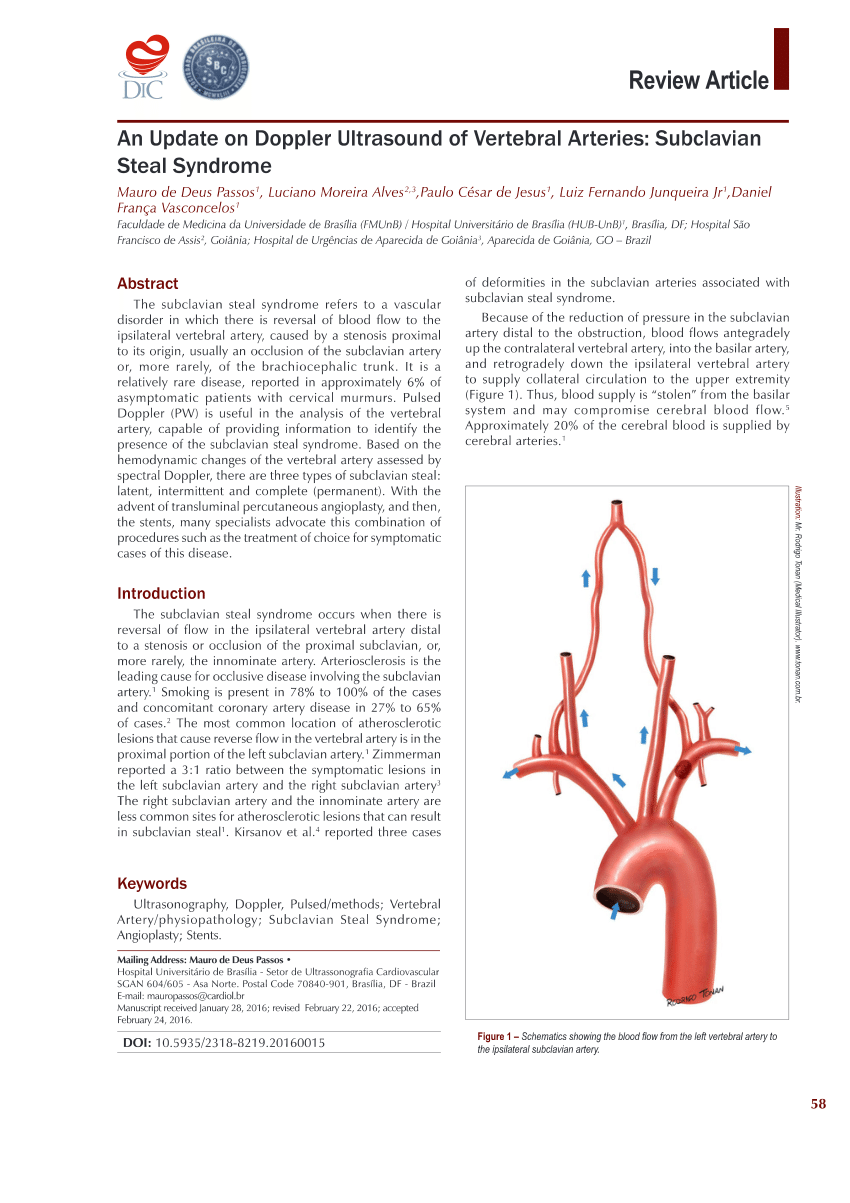
Subclavian steal syndrome SSS is a condition secondary to an occlusion in the proximal subclavian artery which leads to upper-extremity blood supply to be derived by reversal of flow within the ipsilateral VA. Blood is drawn from the collateral circulation which results in reversed blood flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery. The term subclavian steal was coined by Fisher as the reversed retrograde ipsilateral vertebral blood flow was due to the stealing of blood from the posterior cerebral circulation by the subclavian artery.
Patients can present with limb claudication and or cerebral symptoms. Bilateral cervical bruits a difference in blood pressure 4550 mmHg between both arms as well as barely discernable radial ulnar and branchial arterial pulses on the right upper limb prompted color duplex which revealed bilateral internal carotid artery stenosis of 75 at each side retrograde flow in his right vertebral artery subclavian-vertebral steal and retrograde flow in his right carotid artery during the midsystolic phase of the cardiac cycle subclavian-carotid steal. Since recognition of this syndrome can lead to successful treatment a review by.
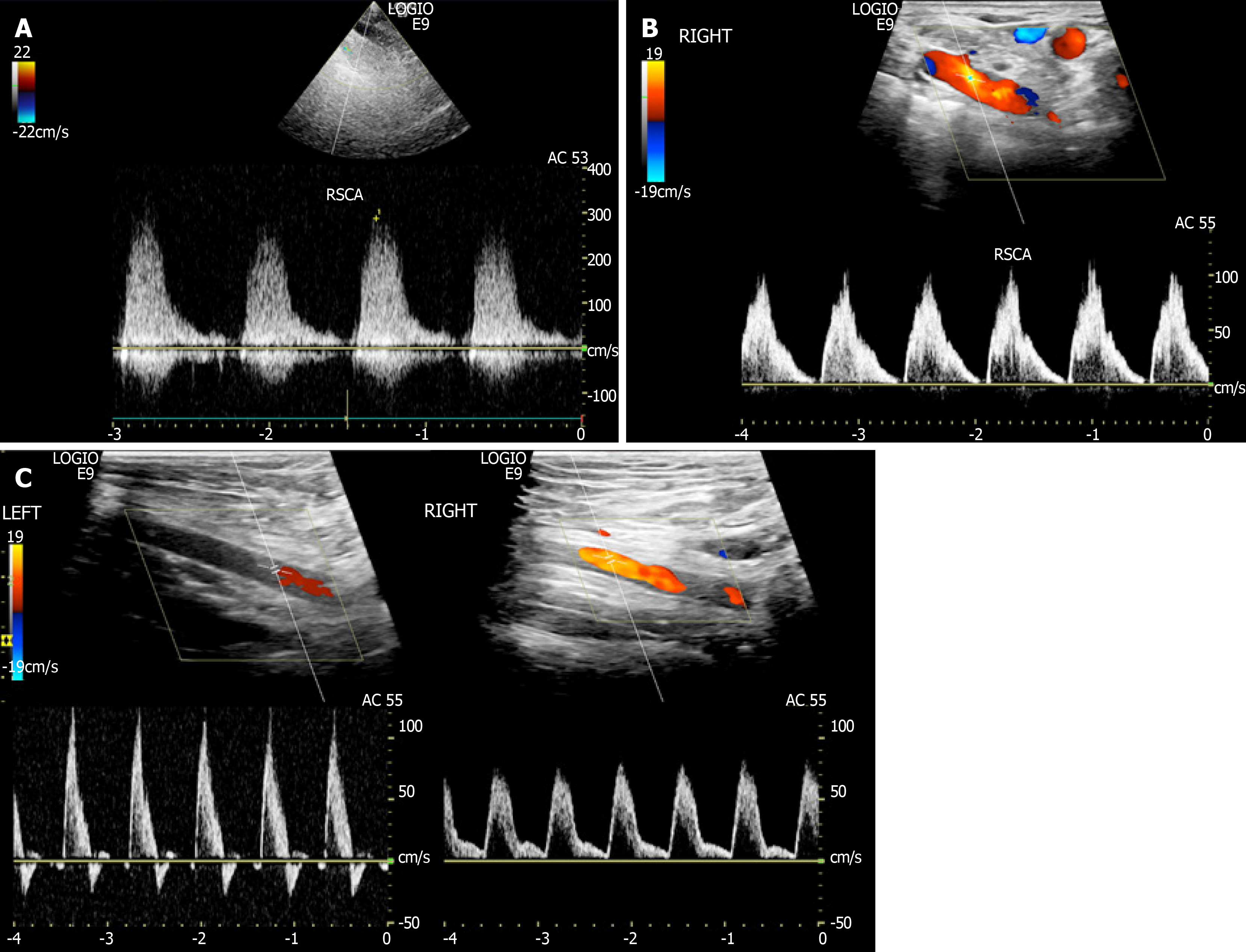
Blood from the contra-lateral vertebral artery is siphoned over at the basilar junction and flows retrograde into the. Right Subclavian Steal Associated with Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery David M.
Features are characteristic of complete left subclavian steal syndrome Features are characteristic of complete left subclavian steal syndrome.
Subclavian steal syndrome SSS is a condition secondary to an occlusion in the proximal subclavian artery which leads to upper-extremity blood supply to be derived by reversal of flow within the ipsilateral VA. Primary Stenting of Right-Sided Subclavian Artery Stenosis Presenting as Subclavian Steal Syndrome. Blood is drawn from the collateral circulation which results in reversed blood flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery. The term subclavian steal describes retrograde blood flow in the vertebral artery associated with proximal ipsilateral subclavian artery stenosis or occlusion usually in the setting of subclavian artery occlusion or stenosis proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. The subclavian steal syndrome is a condition where hypoperfusion of the cerebrovascular system is caused by occlusion or severe obstruction of the proximal subclavian or brachocephalic artery. Alternatively innominate artery disease has also been associated with. Although a low-grade stenosis is usually asymptomatic and may remain unobserved a. The term subclavian steal was coined by Fisher as the reversed retrograde ipsilateral vertebral blood flow was due to the stealing of blood from the posterior cerebral circulation by the subclavian artery. Since recognition of this syndrome can lead to successful treatment a review by.
It is characterized by flow reverse in the vertebral artery to supply the vascular bed distal to the occlusionobstruction and to perfuse the arm collateral flow. The term subclavian steal describes retrograde blood flow in the vertebral artery associated with proximal ipsilateral subclavian artery stenosis or occlusion usually in the setting of subclavian artery occlusion or stenosis proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. Patients can present with limb claudication and or cerebral symptoms. The subclavian steal syndrome is a rare but important cause of syncope. Although a low-grade stenosis is usually asymptomatic and may remain unobserved a. Blood is drawn from the collateral circulation which results in reversed blood flow in the ipsilateral vertebral artery. Features are characteristic of complete left subclavian steal syndrome Features are characteristic of complete left subclavian steal syndrome.















/2019/images/figure1.1564038386.jpg)










.jpg)




Posting Komentar untuk "Right Subclavian Steal Syndrome"